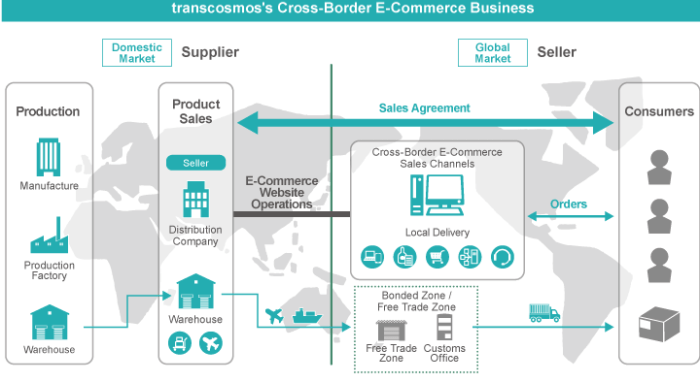
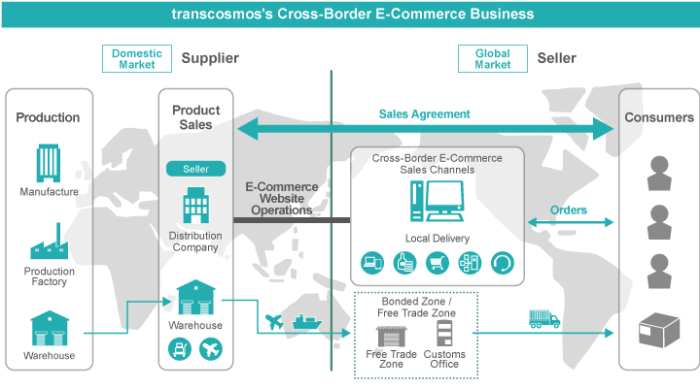
Cross-Border Ecommerce Tax Regulations Explained sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail and brimming with originality. Dive into the complexities of international tax regulations with us.
As we explore the intricacies of cross-border tax laws, we unravel the implications for businesses engaging in global commerce.
Overview of Cross-Border Ecommerce Tax Regulations
Cross-border ecommerce tax regulations refer to the rules and laws that govern the taxation of online transactions between buyers and sellers in different countries. These regulations are put in place to ensure that businesses engaged in international ecommerce activities comply with the tax laws of the countries involved.Countries with strict cross-border tax regulations include the United States, European Union countries, Canada, Australia, and China.
Each of these countries has its own set of rules regarding the taxation of cross-border ecommerce transactions, including import duties, value-added tax (VAT), and customs duties.It is crucial for international ecommerce businesses to comply with these regulations to avoid penalties, fines, or legal issues.
Failure to adhere to cross-border tax regulations can result in costly consequences for businesses, including disruptions to operations, reputational damage, and financial losses. By understanding and following the tax laws of the countries they operate in, ecommerce businesses can ensure smooth cross-border transactions and maintain compliance with local tax authorities.
Types of Cross-Border Ecommerce Taxes

Cross-border ecommerce transactions are subject to various taxes that differ based on the importing and exporting countries involved. It is essential for businesses engaged in cross-border ecommerce to understand these taxes to ensure compliance and avoid any financial penalties.
Value-Added Tax (VAT)
Value-Added Tax (VAT) is a consumption tax placed on a product whenever value is added at each stage of the supply chain, from production to the point of sale. In cross-border ecommerce, VAT is typically determined based on the location of the buyer, with different rates applied in importing and exporting countries.
Failure to comply with VAT regulations can result in costly fines and potential business disruptions.
Customs Duties
Customs duties are taxes imposed on goods imported into a country. These duties are calculated based on the value of the imported goods and the classification of the products. Cross-border ecommerce businesses need to be aware of the customs duties applicable in both the importing and exporting countries to accurately calculate costs and avoid delays in customs clearance.
Other Taxes
In addition to VAT and customs duties, cross-border ecommerce transactions may be subject to other taxes such as excise duties, sales taxes, and income taxes. These taxes vary depending on the nature of the products being sold and the regulations of the countries involved.
It is crucial for businesses to stay informed about these additional taxes to ensure compliance and avoid any unexpected liabilities.
Compliance Challenges for Ecommerce Businesses
Ensuring compliance with cross-border tax regulations can be a daunting task for ecommerce businesses, given the complexities involved in navigating different tax systems and regulations across various countries.
Determining Tax Rates, Thresholds, and Exemptions
One of the major challenges faced by ecommerce businesses is the difficulty in determining the applicable tax rates, thresholds, and exemptions for international transactions. Each country has its own set of tax laws and regulations, which can vary widely from one another.
This makes it challenging for businesses to accurately calculate and apply the correct taxes to their cross-border sales.
- Businesses need to stay up-to-date with the latest tax laws and regulations in each country they operate in, which can be a time-consuming and resource-intensive process.
- The lack of uniformity in tax rates and thresholds across different countries adds to the complexity, making it difficult for businesses to streamline their tax compliance processes.
- Determining tax exemptions for certain products or services can also be challenging, as these exemptions can vary significantly from one country to another.
Strategies for Overcoming Compliance Challenges
Despite the challenges, there are strategies that ecommerce businesses can adopt to overcome compliance hurdles in cross-border ecommerce:
- Utilize tax automation software: Investing in tax automation tools can help businesses streamline their tax compliance processes and ensure accurate calculations of taxes for international transactions.
- Seek professional advice: Consulting with tax experts or advisors who are well-versed in cross-border tax regulations can help businesses navigate complex tax laws and ensure compliance with the relevant regulations.
- Regularly audit and review tax processes: Conducting regular audits of tax processes and staying proactive in identifying and addressing compliance issues can help businesses avoid costly penalties and fines.
Impact of Cross-Border Ecommerce Taxes on Consumers
When it comes to cross-border ecommerce taxes, consumers are directly impacted in terms of pricing and affordability. The imposition of taxes and duties on imported goods can significantly increase the overall cost for consumers, affecting their purchasing decisions and behavior.
Effect on Pricing and Affordability
- Import taxes and duties can lead to higher prices for products purchased from foreign online retailers.
- Consumers may find it less affordable to buy goods from overseas due to the added costs associated with cross-border taxes.
- The increased prices resulting from taxes can make it challenging for consumers to access a wider range of products that may be cheaper without the additional tax burden.
Influence on Consumer Behavior
- Consumers may opt to purchase similar products from local retailers to avoid the extra costs associated with cross-border taxes.
- The presence of taxes on imported goods can slow down the decision-making process for consumers, as they weigh the additional expenses against the benefits of purchasing from international sellers.
- Some consumers may choose to limit their cross-border online shopping or reduce the frequency of such purchases to manage their overall expenditure in the face of higher costs due to taxes.
Strategies for Managing Cross-Border Ecommerce Taxes
When it comes to managing cross-border ecommerce taxes, businesses need to implement effective strategies to ensure compliance and optimize tax efficiency. Leveraging technology and automation can streamline the process, while developing a tax-efficient strategy is crucial for international ecommerce success.
Role of Technology and Automation
Utilizing technology and automation tools can significantly help ecommerce businesses in managing cross-border tax compliance. From calculating taxes to generating reports, these tools can streamline the entire process and ensure accuracy in tax filings. Automation also reduces the risk of human error, saving time and resources for businesses.
Tips for Developing a Tax-Efficient Strategy
- Conduct thorough research on cross-border tax regulations in target markets.
- Consider setting up a tax-efficient supply chain to minimize tax liabilities.
- Utilize tax planning strategies such as transfer pricing and tax treaties.
- Invest in tax compliance software to simplify tax calculations and reporting.
- Seek professional advice from tax experts with experience in international tax laws.
Wrap-Up
In conclusion, Cross-Border Ecommerce Tax Regulations Explained sheds light on the pivotal role tax compliance plays in the international business landscape. Navigate the world of cross-border taxes with confidence and stay ahead of the regulatory curve.
Common Queries
What are the repercussions of not complying with cross-border tax regulations?
Non-compliance can lead to hefty fines, legal consequences, and tarnished business reputation, jeopardizing the success of international operations.
How do I determine the applicable tax rates for cross-border ecommerce transactions?
Research the tax laws of both the importing and exporting countries, consult tax professionals, and leverage automated tools for accurate calculations.
Are there any exemptions for small businesses in cross-border ecommerce taxation?
Some countries offer thresholds or exemptions for small businesses, but these vary widely, necessitating thorough research and understanding of local regulations.